|
1. CONCEPT
2. ORGANISATION OF A MUTUAL FUND
3. ADVANTAGES OF MUTUAL FUNDS
4. TYPES OF MUTUAL FUND SCHEMES
5. FREQUENTLY USED TERMS
|
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
|
A Mutual Fund is a trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share
a common financial goal. The money thus collected is then invested in capital market
instruments such as shares, debentures and other securities. The income earned through
these investments and the capital appreciation realised are shared by its unit holders
in proportion to the number of units owned by them. Thus a Mutual Fund is the most
suitable investment for the common man as it offers an opportunity to invest in
a diversified, professionally managed basket of securities at a relatively low cost.
The flow chart below describes broadly the working of a mutual fund:
|
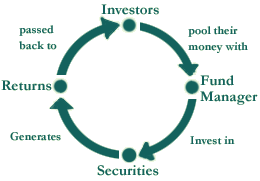
|
|
Mutual Fund Operation Flow Chart
|
|
Top
|
|
|
|
ORGANISATION OF A MUTUAL FUND
|
|
There are many entities involved and the diagram below illustrates the organisational
set up of a mutual fund:
|
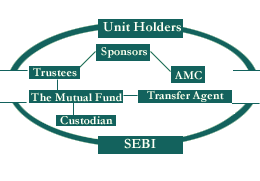
|
|
Organisation of a Mutual Fund
|
|
Top
|
|
|
|
ADVANTAGES OF MUTUAL FUNDS
|
The advantages of investing in a Mutual Fund are:
- Professional Management
- Diversification
- Convenient Administration
- Return Potential
- Low Costs
- Liquidity
- Transparency
- Flexibility
- Choice of schemes
- Tax benefits
- Well regulated
|
|
|
|
Top
|
|
|
|
TYPES OF MUTUAL FUND SCHEMES
|
|
Wide variety of Mutual Fund Schemes exist to cater to the needs such as financial
position, risk tolerance and return expectations etc. The table below gives an overview
into the existing types of schemes in the Industry.
|
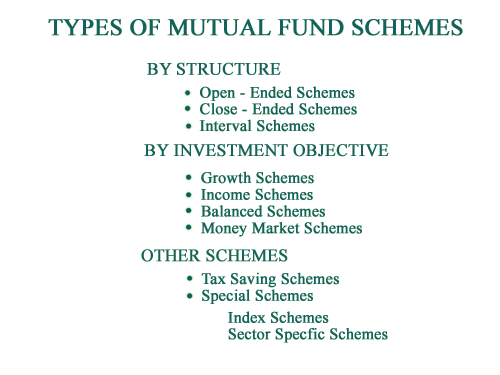
|
|
Top
|
|
|
|
FREQUENTLY USED TERMS
|
Net Asset Value (NAV)
|
|
Net Asset Value is the market value of the assets of the scheme minus its liabilities.
The per unit NAV is the net asset value of the scheme divided by the number of units
outstanding on the Valuation Date.
|
|
|
|
Sale Price
|
|
Is the price you pay when you invest in a scheme. Also called Offer Price. It may
include a sales load.
|
|
|
Repurchase Price
|
|
Is the price at which a close-ended scheme repurchases its units and it may include
a back-end load. This is also called Bid Price.
|
|
|
Redemption Price
|
|
Is the price at which open-ended schemes repurchase their units and close-ended
schemes redeem their units on maturity. Such prices are NAV related.
|
|
|
Sales Load
|
|
Is a charge collected by a scheme when it sells the units. Also called, ‘Front-end’
load. Schemes that do not charge a load are called ‘No Load’ schemes.
|
|
|
Repurchase or ‘Back-end’Load
|
|
Is a charge collected by a scheme when it buys back the units from the unitholders.
|
|
|
|
Top
|
|